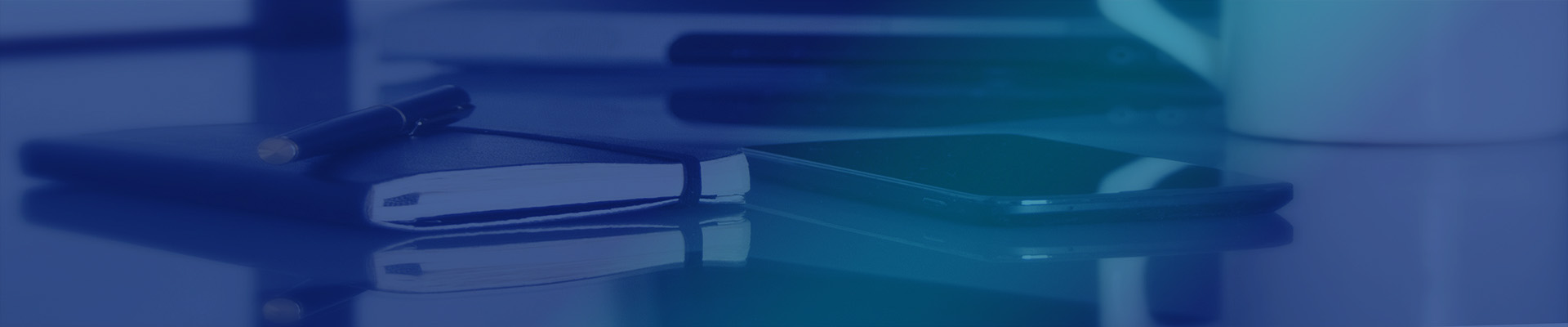

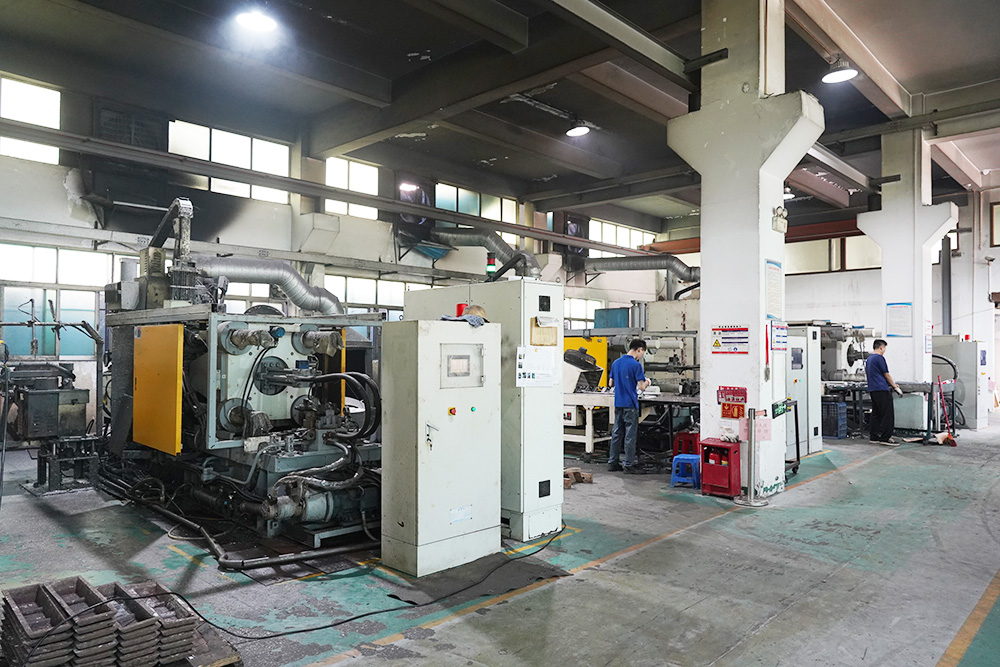
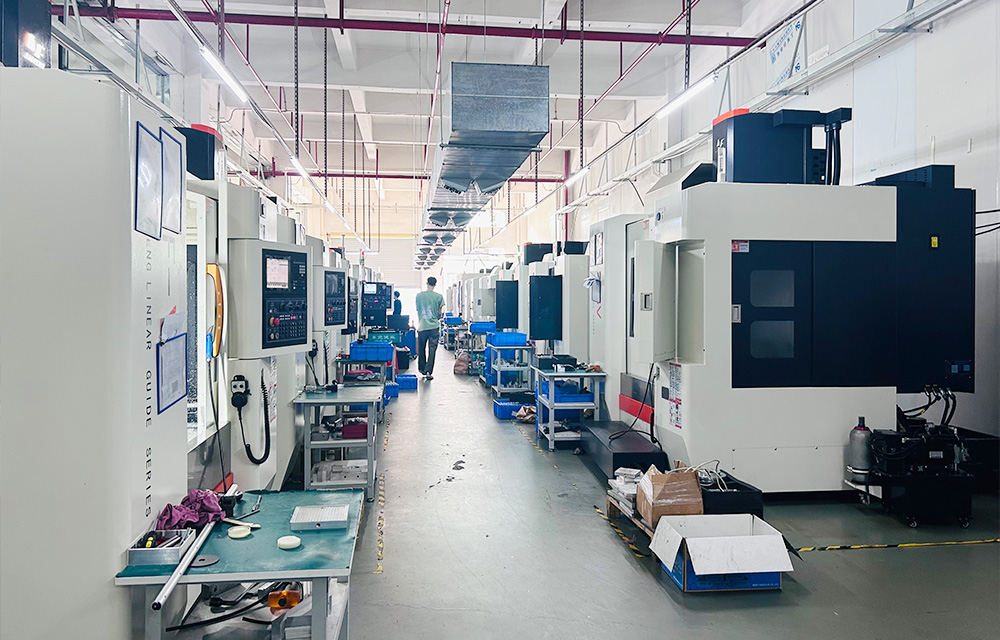
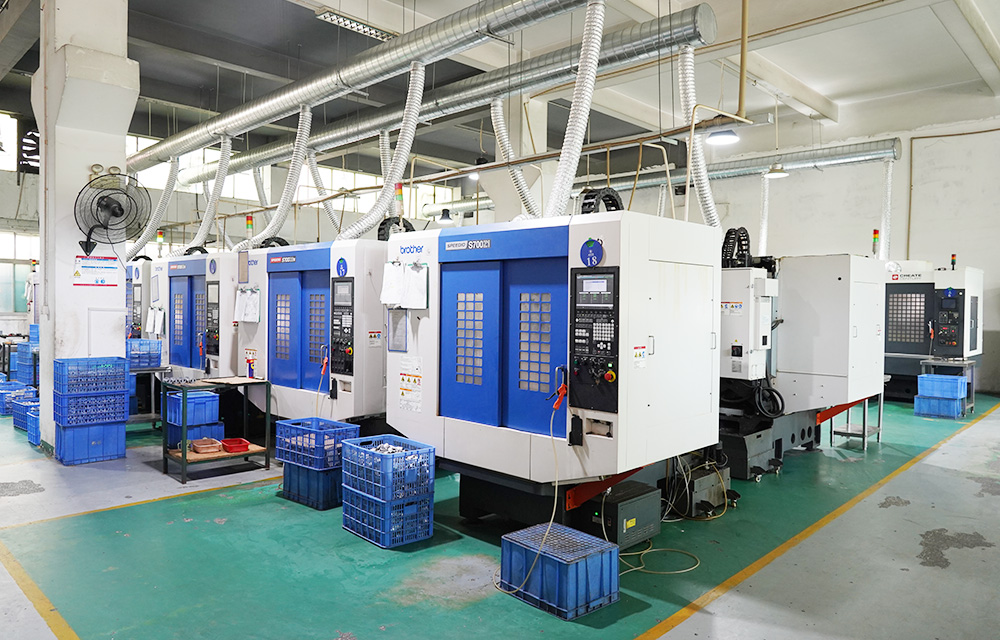
Die casting technology consists of three major elements: machines, molds, and alloys; Unify the process of pressure, speed, and time.
1. Pressure:
It is an important factor in achieving dense structure and clear contour in castings; 2. Injection force: is the force that drives the injection piston in the injection mechanism, calculated in kilonewtons: the tonnage of the machine is 10 to 1, 3. Specific pressure: is the pressure exerted on the molten metal in the injection chamber per unit area, which is the result of the ratio of injection force to the cross-sectional area of the injection chamber. Formula: P ratio=P injection/F chamber P ratio - specific pressure (Pa). The effect and influence of pressure: an increase in specific pressure results in finer crystallization; Thickening of the fine crystal layer improves filling characteristics, enhances surface quality, reduces the influence of pores, but increases tensile strength and reduces elongation.
The influence on filling conditions: Filling the cavity under high specific pressure increases the temperature rise and fall of the alloy, improves fluidity, and is beneficial for improving the quality of castings.
2. Factors affecting stress:
1) The higher the melting point, the greater the effective pressure ratio; 2) The temperature of the alloy liquid is high, the temperature of the mold is too low, and the pressure loss increases; 3) The design of casting structure and pouring system results in higher resistance and lower pressure efficiency; 4) By adjusting the injection force and pressurization system, the injection characteristics can be improved and the quality of castings can be enhanced;
3. Changes in pressure during injection process:
1) Low pressure injection (generally not exceeding 0.3 meters per second), 2) High speed injection (1-5 meters per second), 3) Building pressure 0.05-0.03 seconds, 4 pressure options:
1) According to the strength requirements of the die-casting parts, the specific pressure is selected. Generally, 480 kilograms are used for castings Choose 940 kilograms for castings with high density and force per square centimeter Force/square centimeter, 2), considering the wall thickness of the casting: thin-walled casting - thin sprue, high resistance, and high specific pressure during filling; Thick walled castings - with thick sprues, low resistance, and low specific pressure during filling; Complex shaped castings require consideration of sprue speed, machine clamping force, and mold strength
3) Expansion force and locking force; Partial expansion force, also known as back pressure, is referred to as lateral expansion force in each direction of the sidewall. 5. Injection velocity:
1) Usually, there are two types of injection speed: punch speed and sprue speed. 2) Slow injection speed: the punch pushes the metal liquid to the sprue at a speed of 0.3 meters per second. 3) Fast injection speed: the sprue fills the full cavity at a speed of 4-9 meters per second. With the influence of fast injection, the injection speed is increased, the function is converted into heat energy, and the flowability is good, which is conducive to eliminating defects such as flow marks and cold shuts, improving mechanical performance and surface quality. The selection of injection speed options and factors to consider:
1) Has thermal conductivity and specific heat, with a solidification temperature range.
2) If the mold temperature is low, the speed can be low, otherwise the speed can be high.
3) Complex castings use high-pressure injection speed. Inner gate speed 15-70 meters per second, (metal liquid)
4. The relationship between punch injection speed and sprue speed:
The higher the punching speed, the higher the velocity of the molten metal passing through the mouth.
5. Options for speed selection:
1) The sprue speed is 15-25 meters per second for straight castings, 20-35 meters per second for transverse castings, and 70 meters per second for the inner sprue platform. For thin castings with a thickness of 3 millimeters, the sprue speed is 38-46 meters per second. For thick castings with a thickness of 5 millimeters, the sprue speed is 46-40 meters per second. For thicker castings with a thickness of 5 millimeters or more, the sprue speed is 47-27 millimeters per second. The method of adjusting the regulator is to adjust the injection punch speed, replace the pressure chamber diameter, and change the sprue cross-sectional area.
6. Pressure Measurement and analysis of speed:
1) Die casting parameter tester, first stage, second stage, and boost conversion point time, 2) The influence of boost starting point on die casting quality:
When filling 80% after the start of the first stage, switch to the second stage and boost the starting transition time, and hold the pressure afterwards, otherwise it will affect the quality.
3) The wear and obstruction of the injection punch and the impact of poor injection on the die-casting parameters; 4) Analysis of the causes of wear on the injection chamber and punch:
The clearance between the injection chamber and the punch is less than 0.1 millimeters, and the back and forth friction between the punch and the compression chamber causes high temperature and fragility. As the diameter of the compression chamber increases and the punch becomes smaller, the punch becomes stuck with aluminum shavings, affecting the transmission speed and pressure of the compression chamber without resistance. Therefore, high-temperature resistant lubricating oil should be used for the punch, and cooling water must be opened for the injection rod. At the same time, the punch material should also be selected, generally using ductile iron or beryllium bronze.




Message successfully sent