
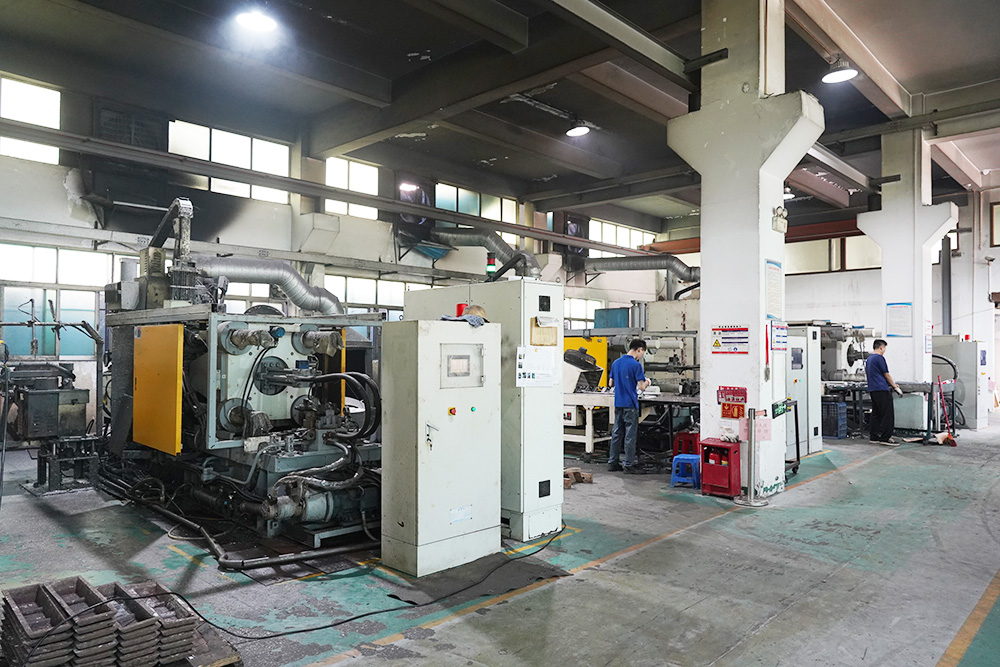
After the 1990s, China's die-casting industry achieved astonishing development and has evolved into an emerging industry. At present, aluminum alloy die-casting technology has become one of the widely used forming processes for automotive aluminum alloys, accounting for 49% of various automotive forming processes.
There are about 3000 die-casting enterprises in China, and the output of die-casting parts has increased from 266000 tons in 1995 to 870000 tons in 2005, with an annual growth rate of over 20%. Among them, aluminum alloy die-casting parts account for more than 3/4 of all die-casting parts production. The types of die-casting products in China are diversified, including automobiles, motorcycles, communications, home appliances, hardware products, power tools IT、 Lighting, escalator steps, toy lights, etc. With the improvement of technology and product development capabilities, the types and application fields of die-casting products are constantly expanding, and their die-casting equipment, die-casting molds, and die-casting processes have undergone tremendous changes. Since its commercial production in 1914, die-casting aluminum alloys have experienced rapid development with the development of the automotive industry and the invention of cold chamber die-casting machines.
Die cast aluminum alloys are divided into two types based on their performance: medium low strength (such as Y102 in China) and high strength (such as Y112 in China). At present, there are several major series of die cast aluminum alloys used in industrial applications, including Al Si, Al Mg, Al Si Cu, Al Si Mg, Al Si Cu Mg, Al Zn, etc. The improvement of mechanical properties of die cast aluminum alloys is often accompanied by a decrease in casting process performance. Pressure casting, due to its high-pressure and rapid solidification characteristics, makes this contradiction more prominent in some aspects. Therefore, it is difficult to perform solution heat treatment on general die cast parts, which restricts the improvement of mechanical properties of die cast aluminum alloys. Although oxygen filled die casting, vacuum die casting, etc. are effective ways to improve the mechanical properties of alloys, there are still certain difficulties in their widespread use. Therefore, the development and research of new die cast aluminum alloys have been ongoing. Advanced die-casting technology: In the early days of horizontal cold chamber die-casting machines, the die-casting process only had one speed to push the molten metal into the mold, and the injection speed was only 1m~2m/s. By using this process, there were many internal pores and loose structure in the castings. Soon after, it was improved to a two-stage injection process, which simply decomposed the injection process into two stages: slow and fast. However, the fast stage was only 3m/s. Later, in order to increase the density of the castings, a pressure boosting stage was added after the slow and fast stages, which became the classic three-stage injection process: slow injection, fast injection, and pressure boosting.
In the mid-1960s, this type of 3-level injection was widely adopted, and the speed of the fast injection stage had increased to 5m/s. During the following 40 years, leading die-casting machine manufacturers from around the world conducted research and experiments on the injection process, thus developing some new processes, such as the parabolic injection system in the 1970s, the no fly edge die-casting system in the 1980s, and the no fly edge injection system in the 1990s. Some of them further decomposed each stage from the three-stage injection, which is an extension of the continued development of this classic three-stage injection. Now the injection speed and pressure have been changed from manual handwheel adjustment control to computer control. In recent years, in order to solve the problems of porosity and shrinkage inside die-casting parts, various high demand die-casting parts with high strength, high density, weldability, heat treatment, and twisting can be produced. In addition to continuing to improve vacuum die-casting, new technologies such as extrusion casting and semi-solid die-casting have been developed, which are summarized as "high-density die-casting method". Vacuum die casting technology is the process of evacuating or partially evacuating the gas in the mold cavity, reducing the gas pressure in the cavity to facilitate filling and removal of gas from the alloy melt, allowing the alloy melt to fill the mold cavity under pressure and solidify under pressure to obtain a dense die casting.
Compared with ordinary die casting, vacuum die casting has the following characteristics: (1) greatly reduced porosity; (2) The hardness of vacuum die cast castings is high, and the microstructure is fine; (3) The mechanical properties of vacuum die castings are relatively high. Recently, vacuum die casting mainly involves extracting gas from the mold cavity, which can take two forms: (1) directly extracting gas from the mold; (2) Place the mold in a vacuum box and evacuate it.
When using vacuum die casting, the design of the exhaust duct position and exhaust duct area of the mold is crucial. There is a "critical area" in the exhaust duct, which is related to the amount of gas extracted from the cavity, the extraction time, and the filling time. When the area of the exhaust duct is greater than the critical area, the vacuum die casting effect is significant; On the contrary, it is not obvious. The choice of vacuum system is also very important, requiring that the vacuum degree inside the mold cavity can be maintained until the filling is completed before the vacuum pump is turned off. The majority of the gas in the pores of die cast parts using oxygen filled die-casting technology is N2 and H2, with almost no O2. The main reason is that O2 reacts with active metals to form solid oxides, which provides a theoretical basis for oxygen filled die-casting technology. Oxygenation die casting is the process of injecting oxygen into the mold cavity before die casting, replacing the air inside. When the molten metal enters the mold cavity, a part of the oxygen is discharged from the exhaust groove, and the residual oxygen reacts with the molten metal to generate dispersed oxide particles, forming an instantaneous vacuum in the mold, thus obtaining a non porous die casting. During the oxygen filled die-casting process, the vacuum inside the mold cavity is generated by a chemical reaction. In order to ensure safety during production, the oxygen filling amount should be strictly controlled, and the cavity pressure should be reduced to match the oxygen filling pressure. Combining vacuum die casting with oxygenation process to keep the mold cavity in a negative pressure state can achieve better results.
During the metal liquid filling process, the metal liquid should be filled in a dispersed spray state. The size of the sprue also has a significant impact on the effectiveness of oxygen die-casting. Appropriate sprue size can meet the requirement of filling the mold with turbulent flow of the metal liquid and avoid the rapid temperature drop of the metal liquid. The highly dispersed distribution of oxides does not have adverse effects on castings, but can instead increase the hardness of castings and refine the microstructure after heat treatment. Oxygen filled die casting can be used for Al, Mg, and Zn alloys that react with oxygen. At present, various aluminum alloy castings can be produced using oxygen die-casting, such as hydraulic transmission housings, heat exchangers for heaters, hydraulic transmission valve bodies, computer brackets, etc. For die-casting parts that require heat treatment or welding, high airtightness requirements, and use at high temperatures, oxygen die-casting has technical and economic advantages. Semi solid die-casting technology is a technique in which liquid metal is stirred during solidification to obtain a slurry with a solid component of about 50% or even higher at a certain cooling rate, and then the slurry is used for die-casting. There are currently two forming processes for semi-solid die casting technology: rheological forming process and thixotropic forming process. The former is to feed liquid metal into a specially designed injection molding machine barrel, apply shear by a spiral device to cool it into a semi-solid slurry, and then perform die casting. The latter is to feed solid metal particles or debris into a spiral injection molding machine, and under heating and shearing conditions, turn the metal particles into a slurry and then die cast into shape. The key to the semi-solid die casting process is to effectively produce semi-solid alloy slurry, accurately control the ratio of solid-liquid components, and research and develop automated control of the semi-solid forming process.
To achieve automated production of semi-solid forming, American scientists believe that the following technologies need to be vigorously developed: (1) rod transportation with adaptability and flexibility; (2) Precise die-casting lubrication and maintenance; (3) Controllable casting cooling system; (4) Plasma degassing and treatment.
Squeezing die casting technology, also known as "liquid metal compression molding". Its castings have good density, high mechanical properties, and no sprues. Some enterprises in our country have applied it in actual production. Squeeze die casting technology has excellent process advantages, as it can replace traditional die casting, squeeze casting, low-pressure casting, vacuum die casting processes, and is compatible with rheological casting processes such as differential pressure casting, continuous casting and forging, and semi-solid processing. Experts believe that extrusion die casting technology is a cutting-edge new technology that spans multiple process fields, with rich connotations, strong innovation, and great challenges.
Electromagnetic pump low-pressure casting is a newly emerging low-pressure casting process, which is completely different from gas low-pressure casting technology in terms of pressurization method. It uses non-contact electromagnetic force to directly act on liquid metal, greatly reducing the problems of oxidation and suction caused by impure compressed air and high oxygen partial pressure in compressed air, achieving smooth transportation and filling of aluminum liquid, and preventing secondary pollution caused by turbulence. In addition, the electromagnetic pump system is completely controlled by computer digital technology, with very accurate and repeatable process execution, which gives aluminum alloy castings significant advantages in terms of yield, mechanical properties, surface quality, and metal utilization. With the continuous deepening of research, this technology has become increasingly mature in terms of technology.
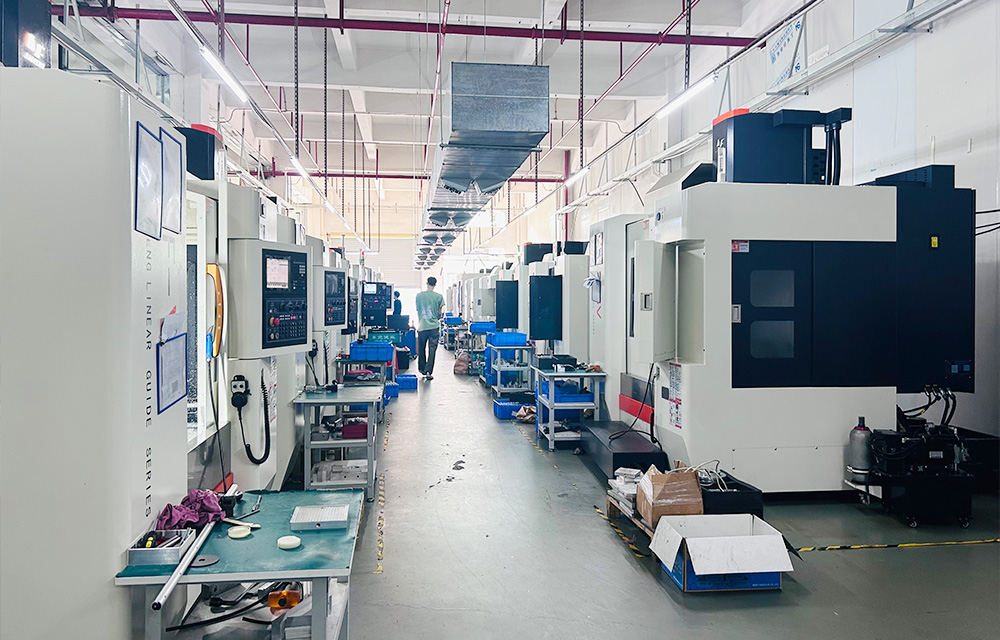
The development of die-casting equipment in recent years has led to varying degrees of improvement in the design level, technical parameters, performance indicators, mechanical structure, and manufacturing quality of die-casting machines in China. Especially for cold chamber die-casting machines, the original fully hydraulic joint mechanism has been changed to a curved elbow joint mechanism. At the same time, automatic loading, automatic spraying, automatic picking, automatic cutting edge, etc. have been added. Electrical appliances have also been changed from ordinary power control to computer control, and the control level has been greatly improved. Some have reached or approached international standards and are moving towards large-scale, automated, and modular production. During this period, new domestic die-casting machine companies emerged one after another, among which Hong Kong Lijin Company is a typical representative. The company has developed multiple leading die-casting models in China, such as horizontal cold chamber die-casting machines with large air injection speeds of 6m/s (1997) and 8m/s (early 2000), magnesium alloy hot chamber die-casting machines with uniform acceleration injection systems (2002), large air injection speeds of 10m/s and multi-stage die-casting systems (June 2004), real-time control injection systems (August 2004), and large die-casting machines with locking forces of 30000kN (July 2004).
In recent years, backbone enterprises such as Shanghai Die Casting Machine Factory and Guannan Die Casting Machine Factory have developed horizontal cold chamber die casting machines with a large air injection speed of 8m/s or more and large die casting machines with a locking force of 10000kN or more; Guangdong Shunwei Yili Precision Pressing Technology Co., Ltd., which was put into operation in 2005, will produce large-scale die-casting machines ranging from 10000kN to 30000kN. It can be seen that China is forming a strong die-casting machine manufacturing industry with independent intellectual property rights. There are currently 12000 die-casting machines in China, of which domestic die-casting machines account for about 85% and imported die-casting machines account for about 15%. In the past two years, the annual sales volume of die-casting machines in China has been above 1800 units, of which 2% are 10000kN and above die-casting machines, 5% are 8000kN~9000kN die-casting machines, 13% are 5000kN~7000kN die-casting machines, 20% are 3500kN~4000kN die-casting machines, and 60% are 3000kN and below die-casting machines. Among die-casting machines below 3000kN, hot chamber die-casting machines account for about 30%.
Small and medium-sized die-casting machines are still dominated by domestically produced equipment. The gap between domestic die-casting machines and advanced die-casting equipment from abroad mainly manifests in the following aspects: (1) outdated overall structural design; (2) Serious oil leakage; (3) Poor reliability: This is a prominent defect of domestic die-casting machines. It is understood that the average time between failures of domestic die-casting machines is less than 3000 hours, and even cannot reach the level of foreign countries in the 1950s and 1960s. And overseas, it generally exceeds 20000 hours; (4) Incomplete variety specifications and poor supporting capabilities: Although a series of horizontal cold chamber die-casting machines have been basically formed, there are still a few gaps, such as no products between 16000kN and 28000kN. The hot chamber die-casting machine also lacks products with a capacity of over 4000kN. The early development of die-casting molds used core materials such as 45 # steel, cast steel, and forged steel. Due to their poor high-temperature impact resistance, their service life was also relatively short at that time. With the development of technology, there have been significant changes in the material of die-casting molds. High temperature and high-strength 3Cr2N8VH13 hot forged steel is now used as the mold core material. In recent years, imported 8407 material has also been adopted, greatly improving the service life of molds. Especially in recent years, most domestic factories have adopted computer design and simulation filling technology, greatly improving the production quality of die-casting molds and shortening the production period.
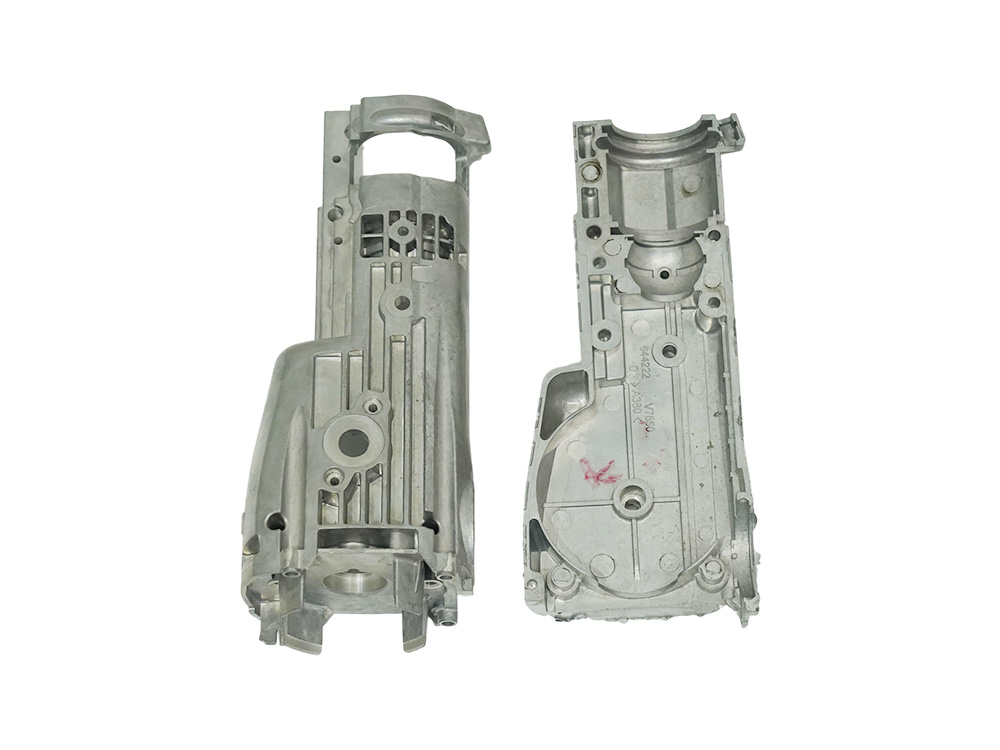
The Chinese mold industry has developed rapidly, with an average annual growth rate of 14% in mold production from 1996 to 2004. In 2003, the output value of die-casting molds was 3.8 billion yuan. At present, the market satisfaction rate of domestic molds in China is only about 80%, with medium and low-end molds being the main ones. Large and complex precision molds cannot meet the needs of national economic development in terms of production technology, mold quality, lifespan, and production capacity. The research and development direction of the automotive and motorcycle industry, as well as the demand for consumption and supporting products of automotive accessories, provides a broad market for the production of die-casting parts, and the application of die-casting aluminum alloys in automobiles will continue to expand.
In the future research and development of die-casting technology, the deepening of aluminum alloy die-casting will still be a major direction for the development of die-casting technology. In order to meet market demand, the following issues should be further addressed in the future: (1) promoting the application of new high-strength and high wear resistant die-casting alloys, researching colorable die-casting alloys, and developing new die-casting alloys for castings with special safety requirements; (2) Develop die cast aluminum alloys with stable performance and easy composition control; (3) Simplify alloy composition, reduce alloy grades, and provide a foundation for achieving green production; (4) Further improve new die-casting processes (vacuum die-casting, oxygen filled die-casting, semi-solid die-casting, squeeze casting, etc.); (5) Improve the ability to quickly respond to the market and promote parallel engineering (CE) and rapid prototyping manufacturing technology (RPM); (6) Conduct research and development on CAD/CAM/CAE systems; (7) Develop and apply more die-casting aluminum alloy automotive parts.




Message successfully sent